Today's business environment is tough, quick to change, and competitive. It is difficult to navigate in this environment without strong leadership abilities.
A leader with a strong set of skills can easily motivate and influence its entire workforce. They also help in transforming an organization.
A leader is like a shepherd. He stays behind the flock, letting the most nimble go out ahead, whereupon the others follow, not realizing that all along they are being directed from behind. - Nelson Mandela.
Successful leaders aren't afraid to get their hands dirty and stand on the front lines.
What is Leadership?
Leadership is a practice or an action that helps an individual to lead a group of people or an organization. It is a skill or an ability of an individual to influence or guide other individuals.
Practice leads to mastery. The same can be said for leadership.
The word leadership has no universal definition. It depends on why and who you ask.
According to circumstances, the meaning differs from person to person. So it depends on personal perspectives.
For some, it is about achieving successful results. For others, it might be gaining power. Being a leader entails putting your team over everything else.
Definitions of leadership differ according to different -
- Theories.
- Models.
- Philosophical Frameworks.
Leaders don’t look backward to condemn what has already been done; they look forward to creating a better future.- Mark Cuban.
Various scholars and authors have defined it in many ways. It is based on their real and personal experiences. Let us look at a few of the definitions.
9 Leadership Definition by Famous Scholars.

- Leadership is not a person or a position. It is a complex moral relationship between people, based on trust, obligation, commitment, emotion, and a shared vision of the good. - Joanne Ciulla.
- Effective leadership is not about making speeches or being liked; leadership is defined by results, not attributes. - Peter F. Drucker.
- Leadership is Influence - Nothing More, Nothing Less. - John Maxwell.
- Leadership is like the Abominable Snowman, whose footprints are everywhere but who is nowhere to be seen. - Bennis & Nanus.
- Leadership occurs when one person induces others to work towards some predetermined objectives. - Massie.
- Leaders are those who consistently make effective contributions to social order, and who are expected and perceived to do so. - Hosking.
- Leadership is a combination of strategy and character. If you must be without one, be without the strategy. - Gen. H. Norman Schwarzkopf.
- Leadership is a function of knowing yourself, having a vision that is well communicated, building trust among colleagues, and taking effective action to realize your leadership potential. - Warren Bennis.
- Leadership is a process of giving purpose (meaningful direction) to the collective effort and causing willing effort to be expended to achieve a purpose. - Jacobs & Jaques.
Each of these authors has their individual working definition of a leader. Hence, it is essential to find out your best definition.
To figure this out, think about what kinds of questions you want to ask about leadership.
Check out our 150 Leadership Quotes to inspire the leader within you.
How does Leadership Work?
The importance of a leader is immense, especially in the corporate context. Every business values’ performance. Hence, leaders are also expected to increase the company’s profit.
Leadership effectiveness may refer to the career success of an individual leader, performance of a group and leader emergency.
In a corporate environment, leaders are evaluated by their effectiveness. However, measuring the effectiveness of a leader differs by their leadership style, behavior, and skills.

What are Leadership Styles?
Leadership Styles are the methods that leaders take to motivate, lead and implement plans. It provides direction to their team.
Different types of styles coexist in working environments. Every style has its advantages and disadvantages.
There is no one best suitable style. It depends on the organizational goal and culture.
Several studies highlighted the distinct styles based on their approaches and how they are viewed by their teams. These styles also help identify leadership behaviors.
What are Leadership Behaviors?
Leadership Behaviors are the personality traits, characteristics, and qualities of a leader. These behaviors lead to an individual's success as a leader.
These behaviors are primarily divided into two types -
-
People-oriented leader’s behavior - These types of leaders concentrate on leader-member relationships. They demonstrate consideration and support for others. They are better at building trust and loyalty. They are also called relationship-oriented leaders.
-
Task-oriented leader’s behavior - These types of leaders concentrate on processes, defined goals, and structures. They stick to rigid schedules and prioritize achieving outcomes.
What is a Leadership Skill?
These are the skills that are necessary in order to organize other people to reach a shared goal.
Decades ago, leadership skills were divided into three types:
- Interpersonal skills.
- Technical skills.
- Conceptual skills.
These skills represented the knowledge and intelligence of a leader. As a result, leaders attempt to learn them in order to grow.
Difference between Leaders and Managers.
Leaders and managers both play an essential role in building a business. Effective leadership can help businesses to reach their goals.
However, being a manager and leader isn't the same. For example, someone who overlooks an organization is not termed as a manager. Executives are a more apt job title.
Leaders are people who do the right thing; managers actually are people who do things right - Professor Warren G. Bennis.
It is a misconception that anyone in a management role is a leader.
Here are their major differences -
| Leader | Manager |
|---|---|
| They focus on setting visions. They bring their vision to reality by motivating others. | They focus on organizational goals. They fulfill the actual tasks and responsibilities of the organization. |
| They lead people and influence them to look at the bigger picture. The focus is on the future. | They may lead a team, but they focus on the smaller goals. The focus is on the present. | Leaders tend to take risks. They try to create something new. | Managers do not take risks as they are more focused on eliminating risks and pitfalls. They maintain the status quo and stability. |
| Leaders focus on the long term. | Managers focus on the short term. |
| Leaders focus on relationships and individualism. | Manager’s work primarily focuses on structures and processes. They help achieve the company goals. |
| Leaders inspire people to follow them. They use personal power. | Managers direct people to get a high level of performance. They use position power on relevant parties. |
| People work under a leader because they are inspired by them. | People work for a manager because they want to impress them. |
| Create a culture based on shared values. | Maintain existing structure. |
It is essential to have managerial skills to become an effective organizational leader.
Most managers have the authority to ensure that tasks are completed effectively. Leaders should be able to take responsibility for managing everything, including trusted managers. But this does not apply to managers.
Managers can evolve into future leaders by developing the necessary skills.
Earlier, it revolved around just three categories. Political, Military, and Religious. However, with the rise of the Industrial Revolution, economic and scientific leaders came into the picture.
The importance of Psychology and Psychiatry in the workplace came into existence. Studies showed that “positive reinforcement in work environments” enhanced consistent productivity.
Leaders with the right attitude and influence made employees feel appreciated and happy in the workplace. In contrast, employees who were not respected didn’t perform well.
Variation in employee performance gave rise to the importance of employee job satisfaction. It also gave rise to employee appreciation.
Evolution of Leadership Theories.
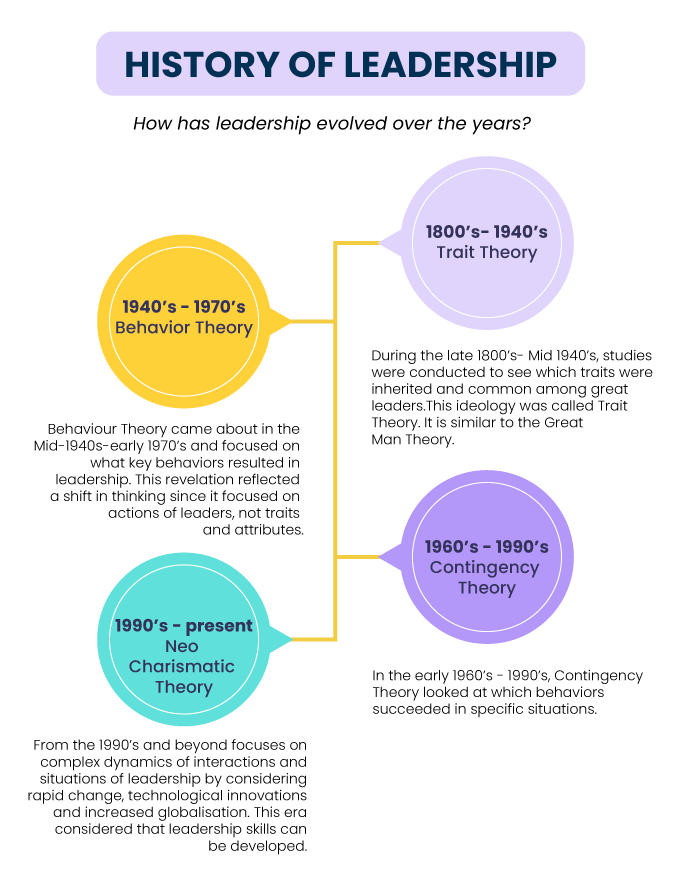
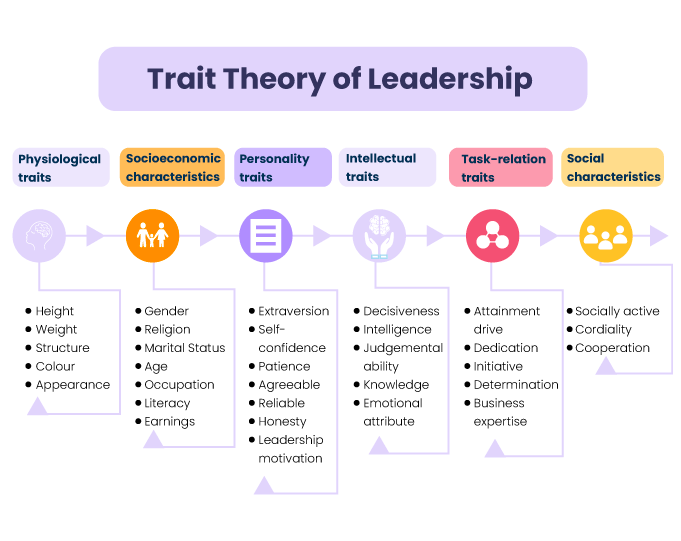
The history of leadership theories is divided into four general eras - Trait era, Behavioral era, Contingency era and New era
The Trait Era.
The Trait era started in the late 1800s and lasted till the Mid-1940s. Researchers of this period supported the belief that leaders are born rather than made. Thus, it is also called the Great Man Theory. The Great Man Theory was first proposed by Thomas Carlyle.
Many such books and articles reveal this era’s belief. Books like Heroes and Hero Worship by Thomas Carlyle (1907), Great man of history by William James (1880), and Role of Heredity by Galton (1869).
The various historical records of that era also showed evidence of this belief. Moreover, the social structures of that period reinforced this belief. They provided limited opportunities to ordinary people to become political, or industrial leaders.
It is said that great leaders are born, not made. The saying is true to this degree that no man can persuade people to do what he wants them to do. Unless he genuinely likes people, and believes that what he wants them to do is to their advantage. - Bruce Fairchild Barton.
Many researchers studied this belief to understand its effectiveness which was inspired by Carlyle’s ideas. According to Carlyle's theory, leadership was based on the rationale that:
- Certain traits produce certain patterns of behavior.
- Patterns are consistent across different situations.
- People are "born" with leadership traits.
However, these common traits didn’t necessarily mean the person was a leader. The characteristic patterns of leaders also differed in different situations.
The Behavioral Era.
The Behavioral era started in the Mid-1940s and lasted until the early 1970s. Researchers in the period supported the belief that leadership is learned.
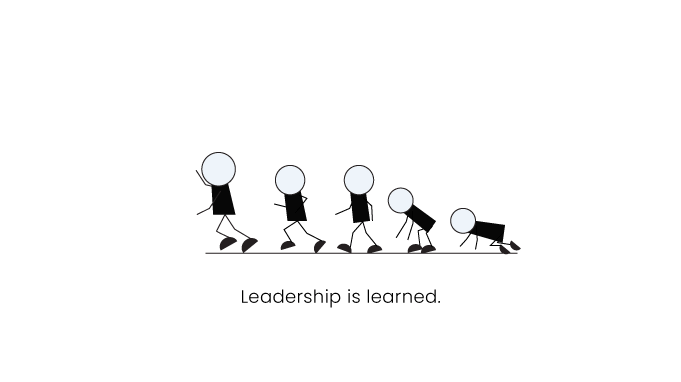
The theoretical approach of this trait didn't work. Hence, there was an urgent need to identify and train leaders during the time of World War II.
To study leaders’ effectiveness, researchers turned towards behaviors. This approach emphasizes what an effective leader does. It does not identify who would be an effective leader.
There were several benefits of this approach over Traits’ Approach.
Hence, the military organizations benefited from behaviors. They could observe, measure and teach behaviors through various measures.
Leadership is learned, earned, and discerned. You develop it. It’s based on trust and credibility. Others see it in you. You can’t demand it. - Rick Warren.
During this era, researchers grouped various leaders’ behaviors. They labeled them Leader’s Styles. Lewin’s early work was concerning these styles. Democratic, Autocratic, and Laissez-Faire or Free-Rein leadership was based upon this approach.
Many researchers continued this study based upon Lewis leader’s styles. Ohio State Leadership studies listed around 2000 leader behaviors. Among them was Task-Relationship behaviors, which was established as the primary leader behavior.
The Ohio State Studies also developed the Leadership Behaviors Description Questionnaire (LBDQ). LBDQ is still used today.
Leadership is a series of behaviors rather than a role for heroes. - Margaret J. Wheatley.
The trait approach was not fully agreed upon by all researchers. The findings did not describe leaders’ behavior adequately for different cultures. It mainly focused on the United States, where values were based upon individualism.
This type of leader’s effectiveness wasn’t enough to express the highly complex nature of the term. Like the Trait Approach, the Behavioral Approach also ignored the situational elements.
The Contingency Era.
The Contingency leadership era started in the early 1960s and lasted until recently around the 1990s. Researchers of this era believed that an effective leader’s personality, style, or behavior depends on the situation they are in.

In the 1960s, Fred Fielder, a leadership researcher-developed one of the first contingency theories. Fielder proposed that each leadership styles were fixed with certain characteristics. Hence, leaders are to be allocated in task situations according to their type of style.
Effective leaders need to be flexible and must adapt themselves according to the situation. - Paul Hersey and Kenneth Blanchard.
Fielder’s Contingency Model determines the effectiveness of a leader. It is determined by how well their style matches the situation they are in.
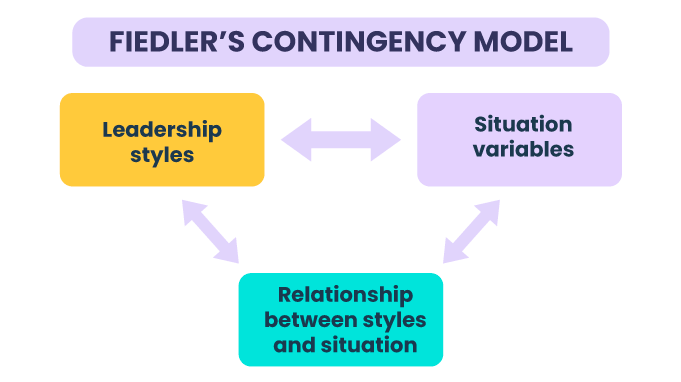
This approach suggests the following:
-
There is no one best set of traits or behavior to lead effectively.
-
The situation and other contextual factors determine which style is most effective.
-
People can learn to become good leaders.
-
Leaders can make a difference in the performance of individuals, groups of people, and companies.
-
Leader effectiveness can get affected due to personal and situational characteristics.
New Era (Neo Charismatic Theory).
The New era of leadership consists of Transactional, Transformational, and other Theories. It started in the 1990s and is continued in the present.
This theory is commonly known as contemporary leadership theory. Today’s researchers believe that one dimension of leadership isn't enough. It cannot cover the complexity that arises from many sources of a company.
The world is constantly evolving. It has become more complex and challenging. This New Era takes into consideration rapid change, technological innovations, and increased globalization.
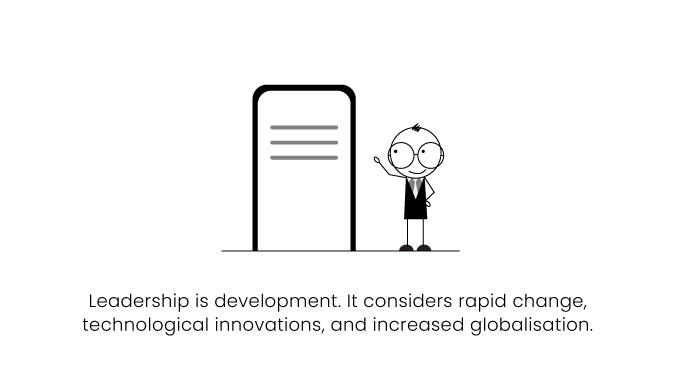
Earlier approaches were traditional and based on leader-follower influences and interactions. This New Era focuses on more complex dynamics of interactions and situations.
This era also considers that leadership skills are present in every individual. But it may not be developed yet. Hence, they believe in development.
Leaders and Managers in the 21st Century.
Early business landscape according to Hitt, Keats, and DeMarie -
-
Firms operated in a relatively smooth landscape
-
Reasonable availability of standard information
-
Fewer variation in international operations
-
Similar accounting practices.
Businesses day to day face numerous changes. These changes occur frequently and are hard to predict.
Successful leaders of this century need to have technical, interpersonal, and cognitive skills. The ideal mix of these skills depends on the company type and the level of management. It also depends on the nature of the challenges they face.
In the current context, effective leaders should have the following skills -
- Analytical ability.
- Persuasiveness.
- Fluency.
- Memory for detail.
- Innovation & cognitive knowledge.
- Technical and conceptual skills.
- Problem-solving skills.
Organizational leadership is a management approach in which leaders help set strategic goals and objectives for an organization. They motivate individuals to fulfill a common task and company goals.
Leaders of an organization have to work ethically and strategically to overcome challenges. Ethical decision-making helps companies to work effectively in competitive markets.
Strategic leaders are one of the options through which companies can navigate competitive markets and overcome challenges.
Strategic leaders can make strategic decisions that are practical, relevant, and sustainable. They use various strategy frameworks to design strategies. They help meet the critical expectations of the stakeholders.
In addition, these leaders understand the importance of effective communication. They have the ability to successfully communicate their vision to others.
A leadership strategy without ethical clarity produces moral and economic bankruptcy. - Bill Donahue.
A good leader has high emotional intelligence (EI). It helps them understand their emotional states. High EI allows them to gauge the emotions of others in a company accurately.

Good organizational leaders work as change agents and manage organizational change processes. The changing trends of businesses have accelerated after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Life after such high-impact low-probability events proves to be a learning lesson in the workplace. This current issue of the global crisis has given birth to a new world overnight.
Companies are now compelled to review and reevaluate constantly. They review all recent technological advancements, innovations, and customer expectations. Reviewing enables them to understand, adopt and implement changes in their business models.
An excellent organizational leader helps companies to function during these change implications smoothly.
Organizational Challenges of Leaders in the 21st Century.

- Globalization has dawned upon every organization in the post-modern world. It is not prominent in just Large Multinational enterprises.
Globalization has affected local businesses in domestic markets. Technological change has enabled small firms to become players in the international markets.
Globalization has largely been due to worldwide economic development and the opening of domestic markets to foreign firms- Hitt, Keats, and DeMarie.
-
Economic change leads to political instability. Economic development forces politicians to apply new rules. It supports growth and further development.
-
Deal with many stakeholders and contingencies. Also deal with complications in incentive systems, and assessment of different subunits’ performance.
-
Today’s leaders should also embrace technological trends and demographic trends. They should also develop economic, social, and cultural environments.
-
Enormous amounts of information are accessible to managers or CEOs. Hence, true leadership practice is needed.
It is estimated that digital data will grow from 400 billion gigabytes of Web-enabled data in 2013 to 40 trillion gigabytes by 2020 - Gantz and Reinsel.
-
Handling the security concerns of a newly digital workforce.
-
Identify theft and online fraud, which cost billions for organizations.
-
Diversity and inclusion continue to be challenging for organizations.
Such issues compel the development of talent in organizations and harm different levels: performance, work climate and even culture. - Cawsey.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution led to development of many opportunities. Organizations with exemplary leadership skills can take advantage of the new trends. New innovations will help them emerge as a leading player in the market.
The future of Leadership will be all about E- Leadership and teleworking. It is the leadership trait of the new era characterized by the fast development of technology and globalization.
Check out this video of Jacob Morgan as he speaks about the future of leadership trends. Jacob is a keynote speaker, best-selling author, and futurist.
Leadership trends for the future will see the rise of the following -
1. Digital Transformation.
The corporate environment will change over the next 10-15 years. Cloud-based infrastructures and internet-based workflows have changed the view of businesses. However, AI and machine learning are already well-known.
Organizations will be forced to change their business models to match up with the trends. Roles will reposition around elements that require critical thinking and technical expertise. Social skills will also be an essential element.
In order to stand out in a leadership role in today’s digital age, skills have to be upgraded.
You do not want a human to decide if you have cancer. You want a machine to analyze tens of thousands of photographs, your blood samples, CT scans, or MRIs. Machines are spectacularly efficient at delivering results. - Martinez.
Also, check out our podcast on Artificial intelligence and its role in shaping HR and employee experience by Ashish Mediratta. He is the Vice President and Principal, Talent Transformation at Eightfold India.
2. People Analytics.

There will be a significant impact on organizations in the coming decade. Generation Alpha will enter the workforce. Hence, businesses will face challenges while managing multiple generations.
This generation is used to being heard through social media. So, they don’t take hierarchical approaches.
Demographics, social values, institutional changes, environmental changes will occur. People Analytics and Ethics will become more significant.
Ethics is more than just environmental threats. It's also about human rights and equality.
The changing demographics in today’s globalized world are forcing organizations to re-examine who their market is and the changes required in the make-up of such organizations to meet the new demands.- Buhle Dlamini.
3. New Skill Set.
Leaders need to revamp their teams’ skills and groups to take advantage of the new opportunities in the marketplace. Development and growth will help them remain competitive.
21st century job skills needed for the future of work include innovative, adaptive, and collaborative skills. Future leaders need to be open to new ideas and aware of their limitations.
Work from home trends will become the future of work in the future as it provides more flexible working hours. Hence, future leaders should be able to manage that successfully.
The ability to adapt requires several Leadership skills which may previously have been less important. - Rohit Talwar.
Check out our podcast on re-skill and upskill to stay relevant in companies by of Capt. Raghu Raman. He is the former CEO of the National Intelligence Grid and former president of Reliance Industries.
4. Shared Vision.
Leaders of the dynamic organization will need strong visions. It will help them to articulate these visions to the business. Future leaders should be able to break structured processes to transform.
For organizational transformation, visionary leaders are the ideal choice. These leaders inspire and energize the employees to work towards higher goals.
5. Employee Engagement.
Soft skills will be one of the essential traits of future leaders in an organization. The ability to engage employees and allow them to follow their own path will be crucial.
An honest, authentic, resilient, and direct conversation will be essential. It will help design a unique customer, talent experience and demonstrate emotional strength. It will also help to give and accept feedback more frequently.
Authenticity means building one’s legitimacy through honest relationships that promote openness, build trust and elicit enthusiastic support. - Gaurav Chaubey
6. Building Talent through Training, Development, and Recruitment.

Future leaders have to be more critical while recruiting new talents in the organization. They will have to strategically recruit people who are comfortable working in ambiguous environments and thrive on change.
Businesses to acquire these talents have to restructure recruitment processes. Specific advertising body language, intelligent candidate identification, and flexible working environments will be necessary. Also, a good job description will help target change makers.
The key to success will be training and developing the existing and future talents. It will help them to understand new technologies. This will also make them more adoptable towards eventual digitalization.
Future leaders should also be aware of the emotional challenge that will come about digitalization. For example, companies have already started using AI tools for HR.
7. Diversity and Inclusion.

Future businesses will see more diverse teams and inclusive cultures. A study by Forbes shows that 87% of the time, companies make better decisions with various groups. In addition, it delivers 60% better results.
Future leaders with vision should mirror the consumer base of their business. It will help understand customer perspectives.
Check out our blog on Diversity and Inclusion Trends to Look Out for in 2021.
You can have a diverse workforce, but if they don’t feel included and that they can speak up and be themselves at work, then you won’t see the benefit. - CJ Bedford
8. Learning Culture.
A learning culture will become conventional. It encourages employees and organizations to develop knowledge and competence.
Learning cultures will open opportunities for the organization to transform. It will also help adapt to the changing environments.
Future leaders should reinforce training initiatives and get feedback. It can be through regular sessions and polls. They should be supportive towards learning environments by giving recognition to their learning.
Future businesses are likely to install more training and employee development plans.
9. Employee Well-Being.
Historically employee well-being initiatives were not considered so important. But, things have changed, especially after the Covid-19 pandemic.
The future of business shows the importance of a healthy work environment. As a result, companies are forced to invest in employee well-being initiatives.
A corporate wellness platform is a great way to ensure a healthy workforce. Good employee health of an organization boosts organizational performance.
Future leaders should understand the difference between the employees’ physical and mental health. In addition, they should be able to understand employees from a holistic perspective.
Conclusion.
Proper approaches to leadership are imperative for success. Leaders are crucial because of their vision and guidance. They help the management deliver quality and improve performance.
Through the study of leadership, we have seen a variety of attributes and abilities associated with it. These vary from leader to leader.
There are numerous ways to define it. Some theories attempt to explain what differentiates a leader, while some explain how great leaders come to be.
These theories don’t only exist in history. Instead, they are concepts with actionable advice that managers or CEOs of an organization can adopt.
Whether it is learned or something people are born with, it is essential to identify leaders. One way to do this is through games and activities. In addition, continuous development is vital for successful and competitive organizations.
Businesses are digitally changing their environment. Hence, the future of leadership positions is very crucial. They have to ensure that employees are retained, trained, and motivated to succeed.
It is important for future leaders to upgrade their skills to take advantage. Future leaders should ensure implementation of employee well-being resulting in job satisfaction.
They should ensure that they develop the company’s culture for today’s and tomorrow’s global workforce.
Hence, at Vantage Circle, we provide a Simple & Al-powered reward and recognition platform for employee engagement. We provide employee rewards, on-spot recognition, feedback, and wellness solutions.